Setup Files Configuration
Essential configuration files for your Django deployment on Proxmox LXC.
Test SSH Script
GitHub Actions workflow to test SSH connection to your server before deployment.
name: Test SSH Connection
on:
workflow_dispatch:
permissions:
contents: read
actions: read
jobs:
test-ssh:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Test SSH connection
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v1.0.3
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
echo "🧪 Testing SSH connection... Nice"
echo "🎉 Successfully connected to $(hostname)!"
echo "Current user is: $(whoami)"
echo "Current directory is: $(pwd)"Github Setup
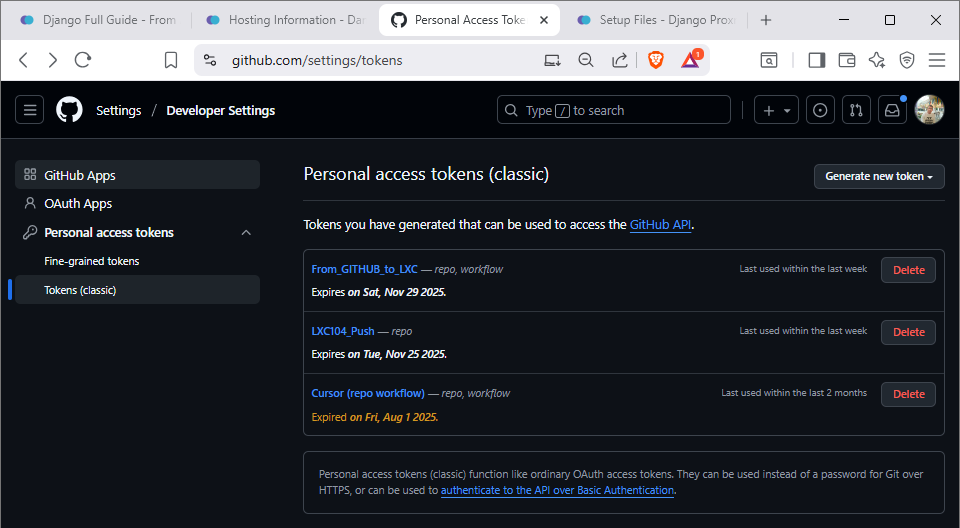
Level Global
Global GitHub App configuration and personal access tokens at the account level.
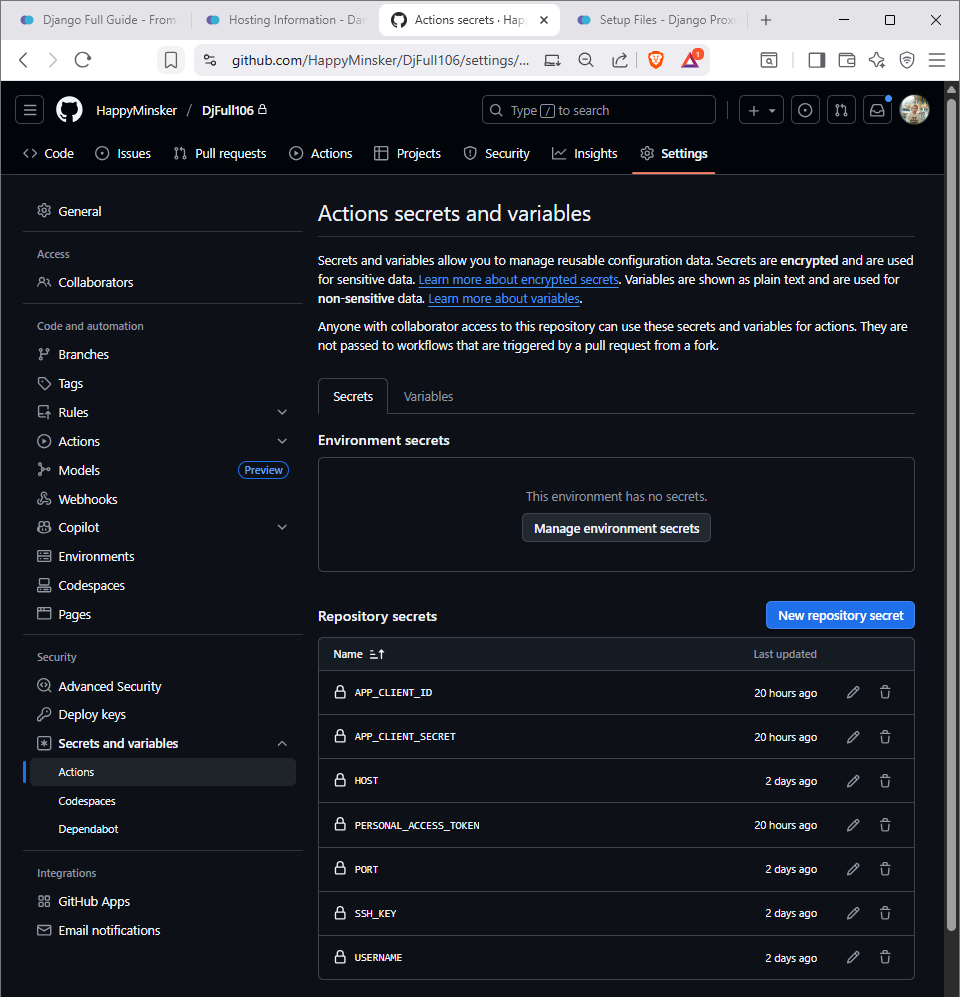
Level Profile
Repository-specific secrets and variables configuration for your project.
Understanding GitHub Setup Levels
Level Global: Account-wide settings that affect all repositories, including GitHub Apps and personal access tokens.
Level Profile: Repository-specific configurations like secrets, variables, and deployment settings that are unique to each project.
Setup Order: Configure global settings first, then set up repository-specific secrets and variables for your deployment workflow.
Detailed GitHub App Setup Guide
Complete setup process: This guide provides step-by-step instructions for setting up GitHub Apps authentication to replace SSH keys.
What you'll accomplish:
- Create a GitHub App with proper permissions
- Generate secure installation tokens
- Configure GitHub Actions secrets
- Update deployment workflow for HTTPS authentication
- Test the complete setup
Prerequisites:
- Access to your GitHub repository settings
- Your server's public IP address (93.125.83.31:8096)
- Admin access to your GitHub repository
Time estimate: 15-20 minutes for complete setup
Next steps: After completing this setup, your deployment workflow will use modern GitHub Apps authentication instead of SSH keys, providing better security and easier management.
SSH Key Setup Guide
SSH Key Setup for GitHub Actions to LXC Deployment
Step 17-1: Configure SSH authentication for automated deployment from GitHub Actions to your LXC container.
Place the PUBLIC Key on LXC108
Prerequisites
Ensure you have generated the GithubToLXC SSH key pair and have access to the public key content.
Copy the Public Key
-
Copy the contents of the
GithubToLXC.pubfile - Keep this content ready for the next step
SSH into LXC108
- Connect using your normal SSH credentials
- Ensure you have access to the user's home directory
SSH Directory Setup Commands
# Navigate to the user's SSH directory
cd ~/.ssh
# If the 'authorized_keys' file doesn't exist, this will create it:
echo "paste_the_public_GithubToLXC_content_here" >> authorized_keys
# Set secure permissions
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysSecurity Notes
Important: The permissions shown above are crucial for SSH security:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh- Only the owner can read, write, and executechmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys- Only the owner can read and write
Warning: Incorrect permissions will prevent SSH authentication from working properly.
Next Steps
After completing this SSH key setup:
- Test the SSH connection from your local machine
- Verify the key is properly loaded in your SSH agent
- Proceed to create the GitHub Actions workflow file
- Configure GitHub repository secrets
.bashrc Configuration
SSH agent auto-start configuration for automatic SSH key loading on login.
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
#if [ -f /etc/bash_completion ] && ! shopt -oq posix; then
# . /etc/bash_completion
#fi
# SSH Agent Configuration
if [ -z "$SSH_AUTH_SOCK" ]; then
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" > /dev/null 2>&1
ssh-add ~/.ssh/Clone_To_LXC106 > /dev/null 2>&1
fi
File Location: ~/.bashrc
What this configuration does: Automatically starts the SSH agent and loads your SSH key when you log in, eliminating the need to manually start the agent each time.
Key features:
- Auto-start SSH agent: Starts ssh-agent if it's not already running
- Automatic key loading: Adds your SSH key to the agent automatically
- Silent operation: Redirects output to /dev/null for clean login experience
- Conditional execution: Only runs if SSH agent isn't already active
How to use:
- Copy the configuration above and add it to the end of your
~/.bashrcfile - Update the SSH key path from
Clone_To_LXC106to your actual key name - Save the file and reload:
source ~/.bashrc - Test by logging out and back in - your SSH key should load automatically
Note: This configuration is specific to LXC106. For LXC108, update the key path to Clone_To_LXC108.
/etc/nginx/sites-available/DjFull108
Nginx configuration for Django application
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
location /static/ {
alias /var/www/DjFull108/staticfiles/;
}
}Nginx Configuration Verification Commands
Commands to verify Nginx configuration and enabled sites (Step 12/5)
root@DjFull108:~# sudo nginx -T | sed -n '1,200p' | grep -E "server_name|listen|sites-enabled"
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
# listen localhost:110;
# listen localhost:143;
# configuration file /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/DjFull108:
listen 80 default_server;
server_name 192.168.1.28;
root@DjFull108:~# ls -l /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 36 Sep 1 08:56 DjFull108 -> /etc/nginx/sites-available/DjFull108
root@DjFull108:~#gunicorn.service
Gunicorn systemd service configuration
[Unit]
Description=Gunicorn daemon for Django
After=network.target
[Service]
User=root
Group=root
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/DjFull108
ExecStart=/var/www/DjFull108/venv/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind 127.0.0.1:8000 DjFull108.wsgi:application
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=mixed
TimeoutStopSec=5
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
File Location: /etc/systemd/system/gunicorn.service
What this file does: This systemd service file tells your server how to run the Gunicorn WSGI server for your Django application.
Key configuration details:
- Working Directory:
/var/www/DjFull108- Where your Django project is located - User/Group:
root- Runs with root privileges (adjust if needed for security) - Workers:
3- Number of Gunicorn worker processes - Bind Address:
127.0.0.1:8000- Only accessible from localhost
How to use:
- Copy the configuration above and save it to
/etc/systemd/system/gunicorn.service - Reload systemd:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload - Enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable gunicorn - Start the service:
sudo systemctl start gunicorn - Check status:
sudo systemctl status gunicorn
Security note: Consider running Gunicorn as a non-root user for production environments.
DjFull108/settings_production.py
Django production settings file (using SQLite)
"""
Django settings for DjFull108 project in production.
"""
from pathlib import Path
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
SECRET_KEY = 'your-production-secret-key-here'
DEBUG = False
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['93.125.83.31', '192.168.1.28', 'localhost', '127.0.0.1']
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'main',
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
ROOT_URLCONF = 'DjFull108.urls'
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [BASE_DIR / 'templates'],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
WSGI_APPLICATION = 'DjFull108.wsgi.application'
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
}
}
# Password validation
AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
]
# Internationalization
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us'
TIME_ZONE = 'UTC'
USE_I18N = True
USE_TZ = True
# Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
STATIC_URL = 'static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
BASE_DIR / 'assets',
]
STATIC_ROOT = BASE_DIR / 'staticfiles'
# Default primary key field type
DEFAULT_AUTO_FIELD = 'django.db.models.BigAutoField' .github/workflows/deploy.yml
GitHub Actions workflow for automatic deployment
name: Deploy Django to Proxmox Server
on:
push:
branches: [ main, master ]
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Deploy to Proxmox Server
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v1.0.3
with:
host: ${{ secrets.HOST }}
username: ${{ secrets.USERNAME }}
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_KEY }}
port: ${{ secrets.PORT }}
script: |
# Navigate to project directory
cd /var/www/DjFull108
# Pull latest changes from GitHub
git pull origin main
# Activate virtual environment
source venv/bin/activate
# Install/update dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run database migrations
python manage.py migrate --settings=DjFull108.settings_production
# Collect static files
python manage.py collectstatic --noinput --settings=DjFull108.settings_production
# Restart Gunicorn service
sudo systemctl restart gunicorn
# Reload Nginx configuration
sudo systemctl reload nginx
echo "Deployment completed successfully!"
- name: Deployment Status
run: |
echo "✅ Django application deployed to Proxmox server"
echo "🌐 Website should be available at your domain/IP"
echo "📝 Check server logs if needed: journalctl -u gunicorn"